MARRIS MODEL
GOALS OF FIRMS
Profit maximisation – short and long term
Stable dividend payouts
Growth in capital value
Sales revenue maximisation
Maximisation of capital assets
Maximisation of market share
Ethical goals
Price stability
Multiple goals
Satisficing objectives
THEORIES OF THE FIRM
CLASSICAL
ass. Simple maximisation approach (profits)
MANAGERIAL
ass. Constrained maximisation approach
- Baumol
- Marris
- Williamson
AGENCY
ass. Firm represents contracts as between principal and agents
BEHAVIOURAL
ass. Satisfying approach
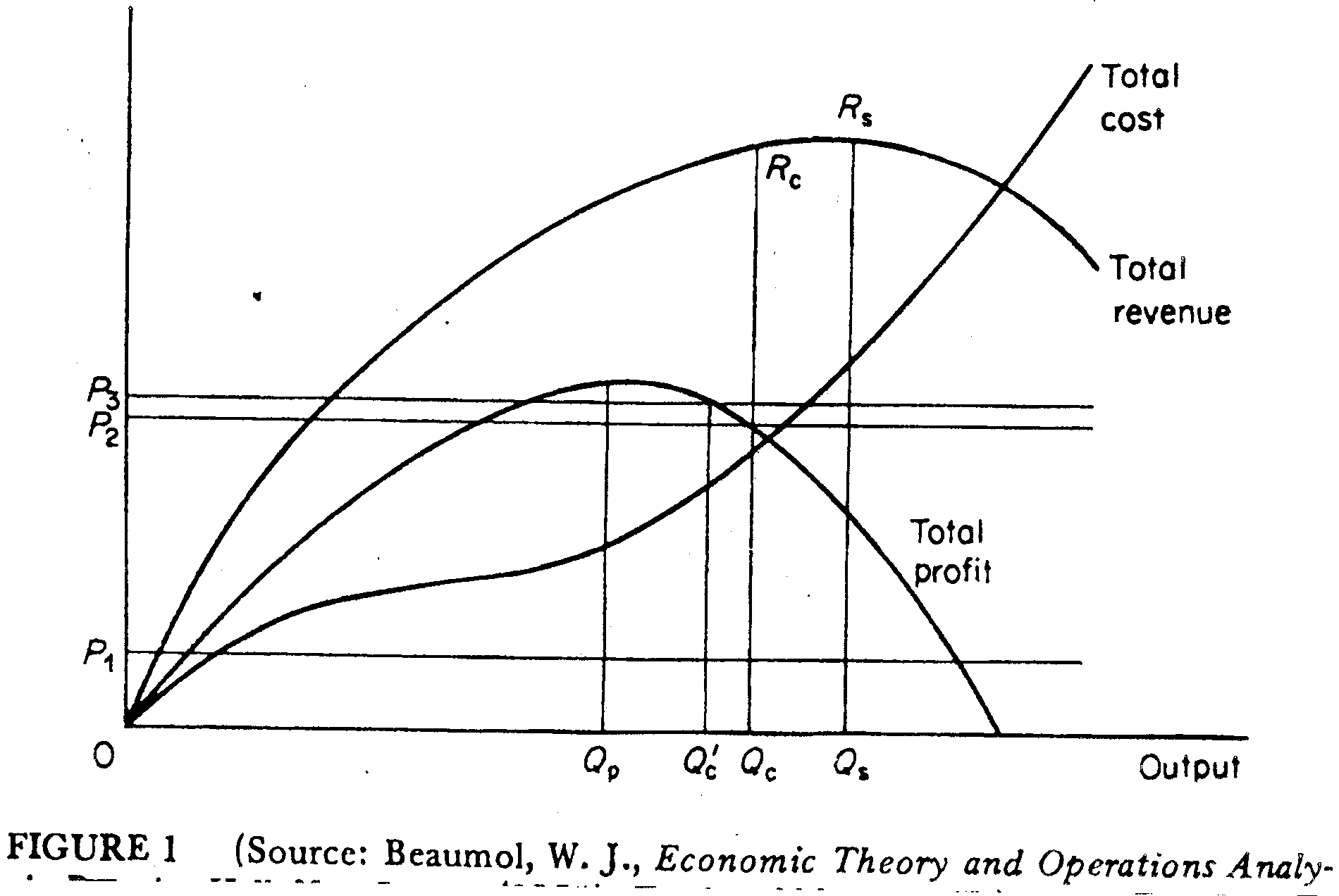
BAUMOL MODEL
Assumption: to maximise sales subject to a profits constraint
Leads to a higher level of output than in the simple maximisation approach

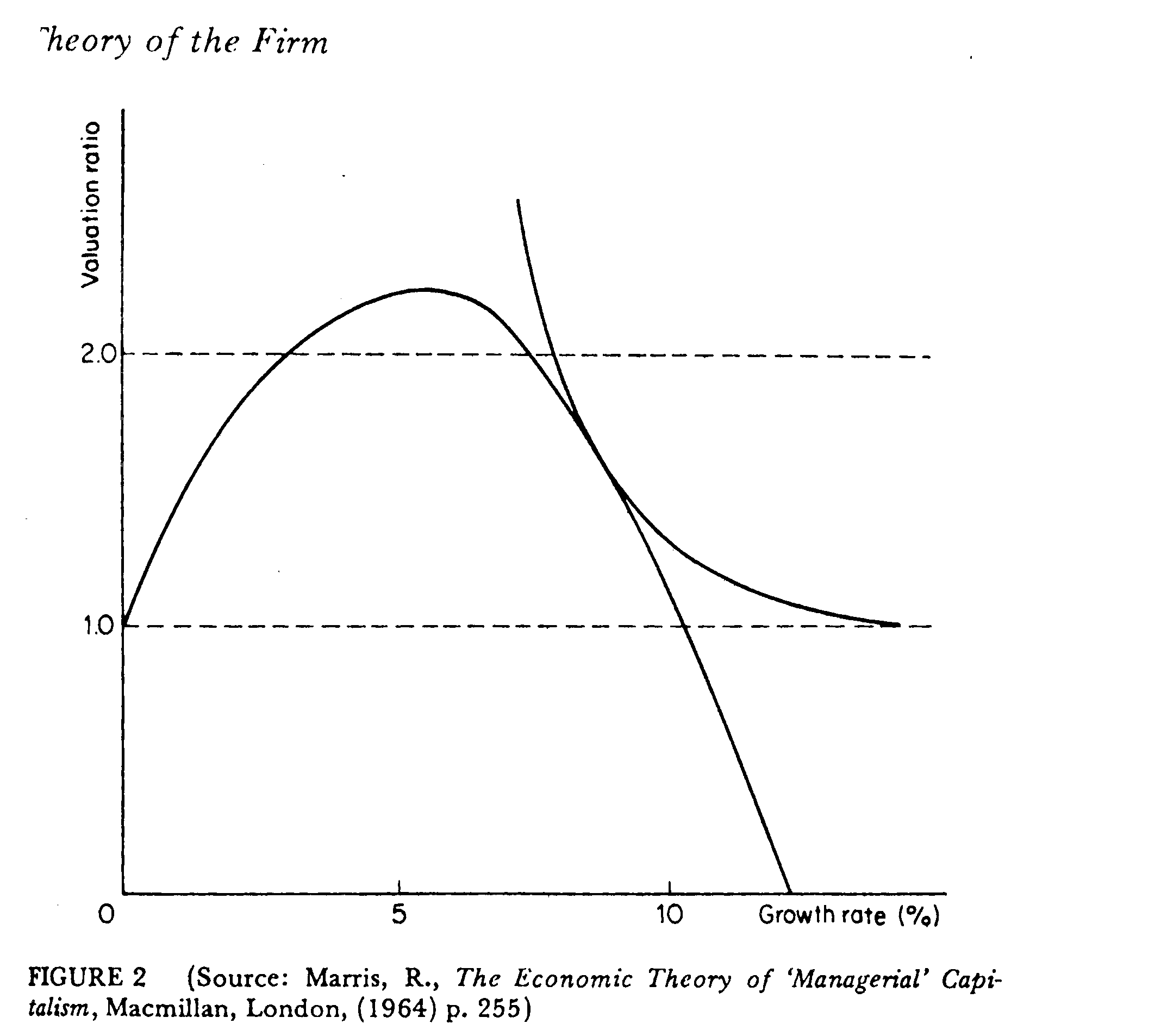
MARRIS MODEL
WILLIAMSON MODEL
Managerial Goals
OTHER GROWTH MODELS
- technostructure
- technology restraint
- transfer and innovation mechanisms
- managerial restraint
- resources and services
- role of diversification
- internal and external obstacles
- internal and external opportunities
BEHAVIOURAL THEORY OF
THE FIRM
Based on coalition of different
interest groups
Stakeholders:
Shareholders
Management
Workers
Bankers
Customers
State
Suppliers
Satisficing Behaviour
- examples of compromise
BEHAVIOURAL THEORY
Organisation seen as coalition
of differing interest groups
MANAGERS SUPPLIERS
SHAREHOLDERS CUSTOMERS
WORKERS GOVERNMENT
SUB GOALS
PRODUCTION
MARKET SHARE
INVENTORY PROFIT
SALES
MAIN CONCEPTS
SIDE PAYMENTS
SEQUENTIAL V SIMULTANEOUS ACTIVITY
ORGANISATIONAL SLACK
ASPIRATIONS AND NON OPERATIONAL GOALS
SATISFICING BEHAVIOUR
SEARCH ACTIVITY
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES
SUMMARY
QUASI RESOLUTION OF CONFLICT
UNCERTAINTY AVOIDANCE
PROBLEMISTIC SEARCH
ORGANISATIONAL LEARNING
CRITICISMS
TOO SHORT TERM
VIEWS FIRM TOO PASSIVELY
LACKS PREDICTIVE VALUE